BioDiamond
Problem and Solution
The Problem
Restenosis, acute and sub-acute thrombosis - persistent complications in interventional cardiology
The Solution:

- coated with Diamond-Like Carbon by Plasma-Induced Cold Deposition
- profiled wall thickness by BioDiamond electropolishing
- dense D- and flexible F-segments in the BioDiamond Stent design
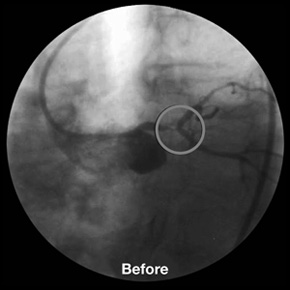

LMCA Y-Stenting with 3 BioDiamond stents.
9 x 3.5 mm distal LMCA,
9 x 3.0 mm ostial LAD and
9 x 3.0 mm ostial Cx.
CHP Beauregard, Marseille
Why are BioDiamond Stents so special?
Disadvantages of conventional stents
- Heavy Metal Ions: Stent alloys release cytotoxic heavy metal ions, potential inducers of allergies, clotting, immune reactions and hyperproliferation of smooth muscle cells.
- Protein Absorption: Metal surfaces efficiently absorb and denature proteins, potentially activating immune responses, allergies, platelets and clotting factors.
- Lack of Bio- and Haemocompatibility: Metal surfaces inhibit growth and adhesion of endothelial cells and activate granulocytes and platelets.
- Induction of Trauma During Deployment: Standard designed stents might open at the ends during balloon dilatation, thus causing thorn-trauma of vessel´s intima by pins located at both ends of the stent.
Advantages of BioDiamond Stents
- Significantly reduced release of heavy metal ions: Uniform coating of the inner and outer stainless steel surface with Diamond-Like Carbon by a specially developed Plasma-Induced Cold Deposition Technique (PICDT allows to provide high quality uniform coating inside the stent, thus overcoming the Faraday cage effect) inhibits the release of cytotoxic and allergenic heavy metal ions from metal surface into the surrounding tissue and blood.
- The Diamond-Like Carbon coating is ultra-thin (50 nm), extremely sturdy, smooth and flexible. It will not crack during stent deployment and is highly resistant even to strong acids like 1 N HCl.
Less Restenosis and Thrombosis by Enhanced Haemo- and Biocompatibility of BioDiamond Stents

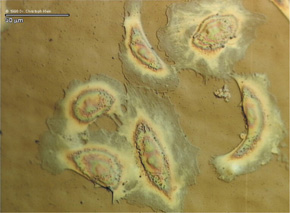
Human Endothelial Cells adhere better on Diamond-Like Carbon (right) than on stainless steel (left).
Notice that on stainless steel pseudopodia (red arrows) are formed and that the cytoplasmic offshoots are much thinner than on diamond. Shearing experiments reveal a significantly stronger adhesion of cells on diamond in comparison to metal.
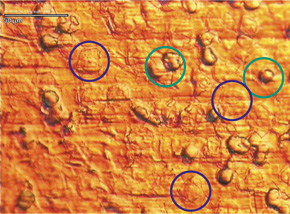
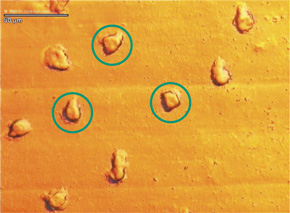
The immune system responds to stainless steel (left) and not to Diamond-Like Carbon (right).
The metal surface is covered with flattened activated granulocytes (exemplary in blue circles) in comparison to the Diamond-Like surface with inactivated round granulocytes (exemplary in green circles). Data and photographs from Dr. C. Klein, University of Mainz.
